Introduction to Gestalt Psychology
Gestalt psychology, a school of thought in psychology, emphasizes understanding the whole of experience rather than its parts. Originating in the early 20th century with thinkers like Max Wertheimer, Kurt Koffka, and Wolfgang Köhler, Gestalt psychology focuses on how people interpret the world around them.
Key Principles of Gestalt Psychology
Gestalt psychology is based on the idea that humans inherently perceive things as part of a greater whole and as elements of more complex systems. This approach is encapsulated in the famous phrase, “The whole is greater than the sum of its parts.”
Examples and Applications
Figure-Ground Perception:
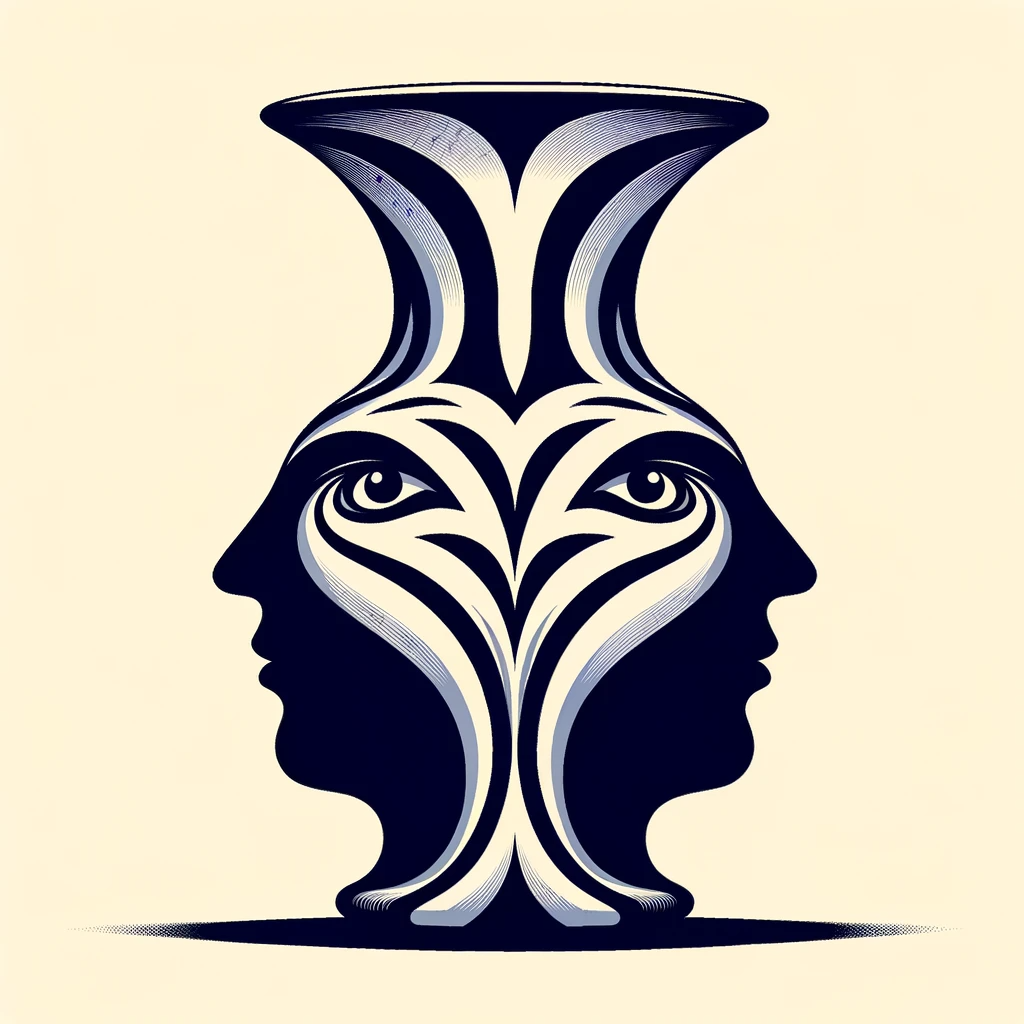

This is a famous image that can be seen in two ways: either as a vase or as two faces looking at each other. The figure-ground principle illustrates how our perception can shift between the object (the vase) and the background (the faces).
Proximity:
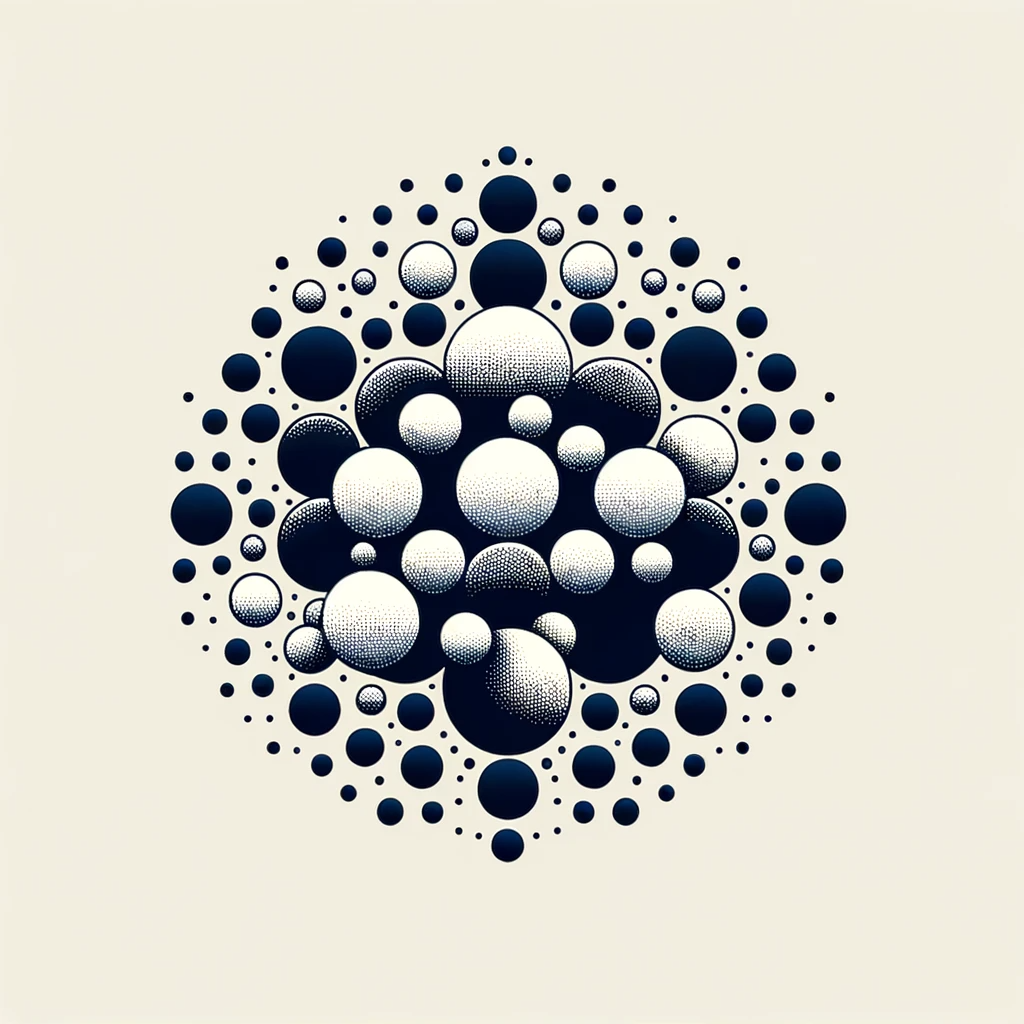
When dots or shapes are placed close together, they tend to be perceived as a group. This demonstrates the Gestalt principle of proximity, where elements close to each other are viewed as a unit or collection.
Similarity:
When circles and squares are mixed in a grid but arranged in rows, people tend to see horizontal lines of circles and squares, not vertical ones. This illustrates how similar objects are grouped in our perception.
Closure:

Even if a shape, like a circle, isn’t completely closed, our perception tends to fill in the missing parts. This principle of closure shows how we perceive complete figures even when part of the information is missing.
Continuity:
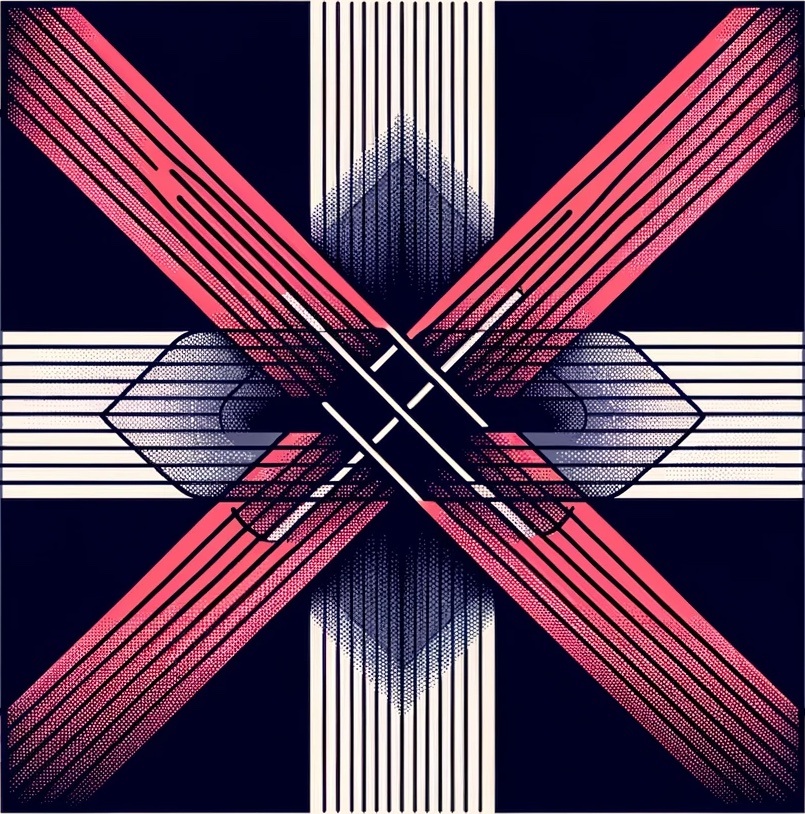

When two lines intersect, we tend to see them as two single straight lines, rather than switching back and forth between the line segments. This demonstrates the principle of continuity, where our mind continues shapes beyond their ending points.
Common Fate:
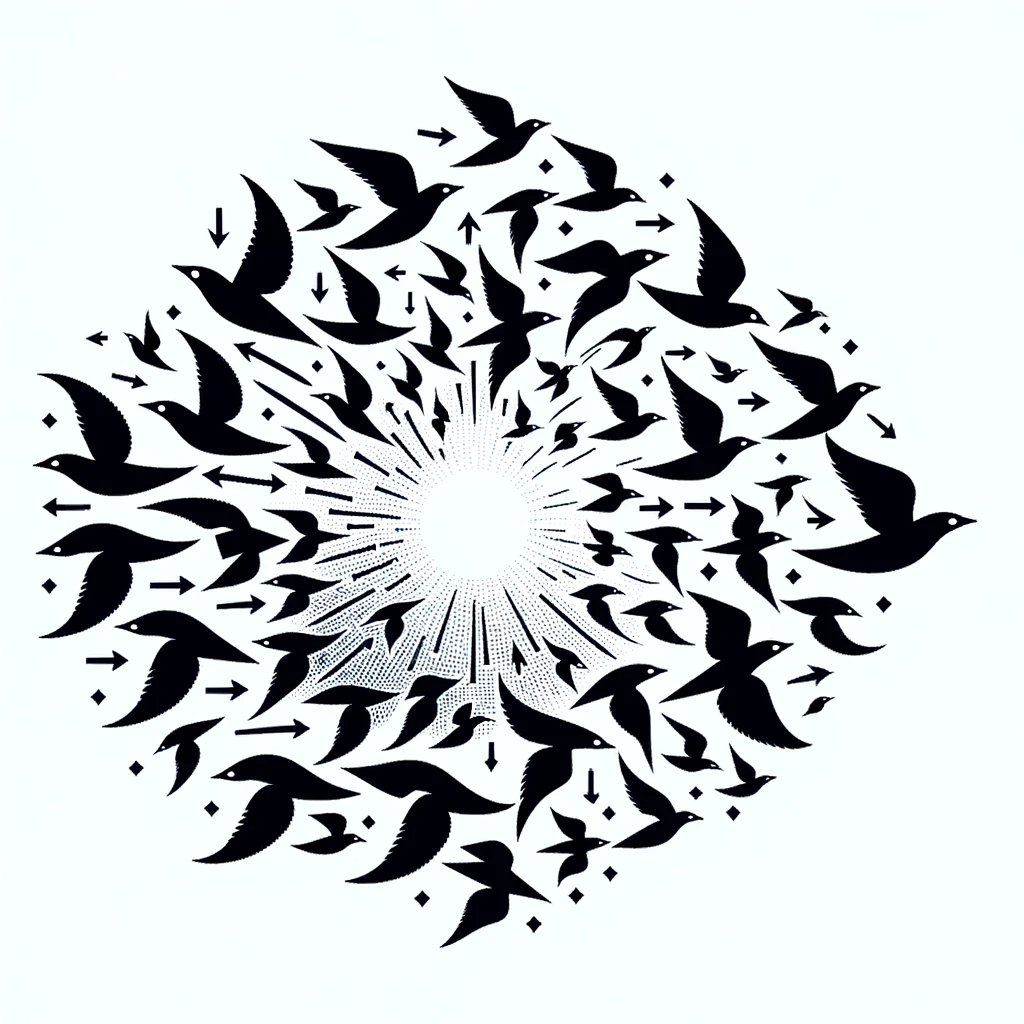

Objects moving in the same direction are often perceived as a group. This principle is observed in nature, like a flock of birds moving together, and illustrates how movement can unify elements.
Statistics and Research
Gestalt psychology has significantly influenced the understanding of human perception. Research in this field has shown that our perception is not just a product of the stimuli in our environment but also of our cognitive processes.
Criticisms and Counterarguments
Despite its contributions, Gestalt psychology has been criticized for its lack of scientific rigor and overemphasis on subjective interpretation. Critics argue that it overlooks the role of learning and past experiences in perception.
Further Reading
- Gestalt Psychology: An Introduction to New Concepts in Modern Psychology by Wolfgang Köhler
- Productive Thinking by Max Wertheimer
Conclusion
Gestalt psychology offers valuable insights into human perception and cognition. Its emphasis on the holistic nature of experience helps us understand how we organize and interpret the world around us, impacting various fields from design to psychotherapy.




