In the ever-evolving landscape of neuroscience, the study of neurons and synapses stands at the forefront, captivating the curiosity of scientists and laymen alike. This modern exploration delves deep into the heart of our neural network, breaking down complex concepts into digestible insights. Welcome to the ultimate guide to understanding the brain’s messaging system.
The Building Blocks of Thought: Neurons
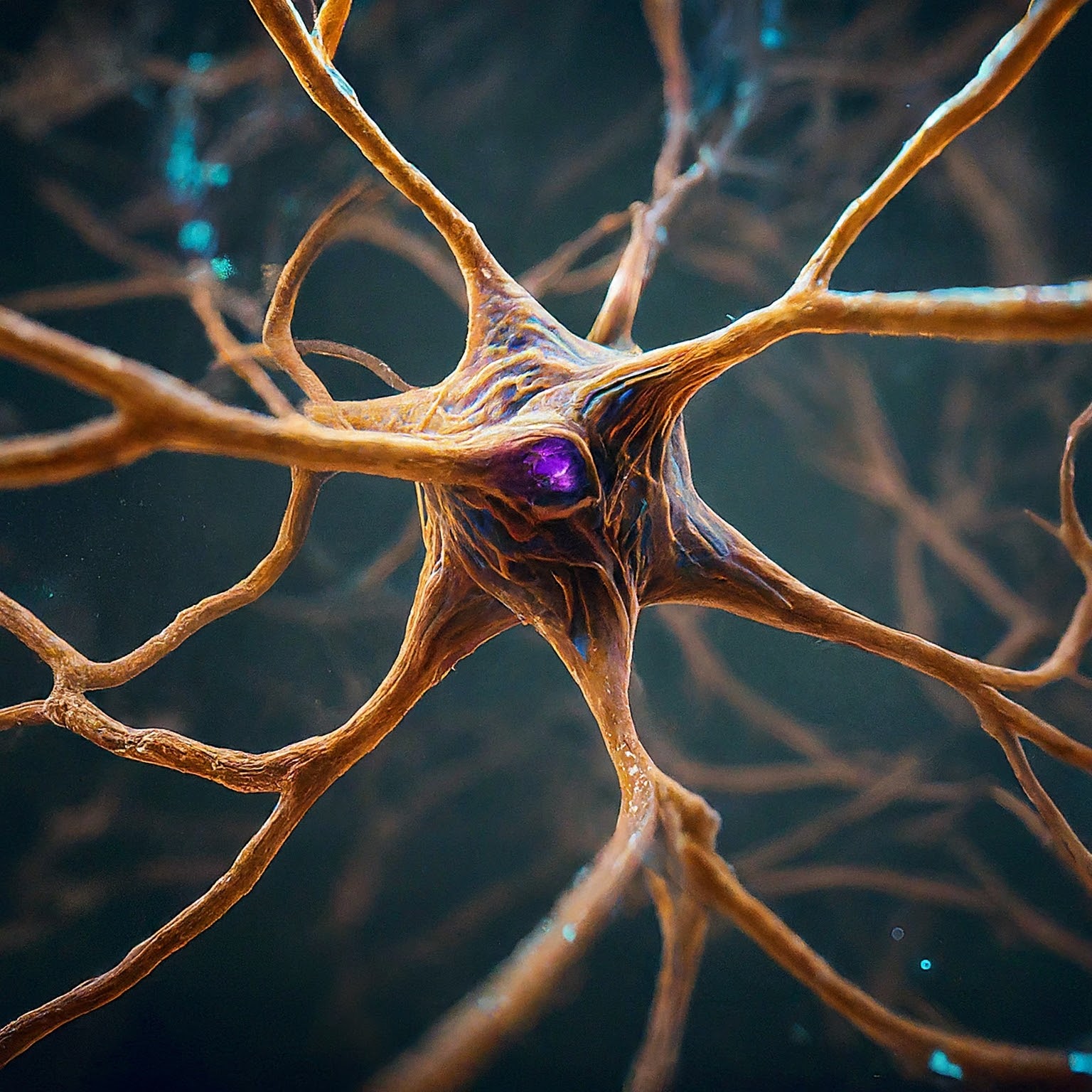
At its core, the human brain is composed of billions of neurons, each a marvel of biological engineering. Neurons are the chief information carriers in the nervous system, designed to transmit signals with astonishing speed and precision. Imagine each neuron as a city within a vast metropolis, interconnected through myriad pathways that dictate every thought, action, and emotion.
The Anatomy of a Neuron
A neuron’s structure is uniquely suited to its role. It consists of three main parts:
- The Cell Body (Soma): The neuron’s headquarters, housing the nucleus and the machinery for the cell’s survival.
- Dendrites: Branch-like structures that receive messages from other neurons, akin to inboxes for incoming mail.
- Axon: A long, slender projection that sends messages out to other neurons, effectively the neuron’s broadcasting tower.
The Synapse: Where Communication Happens
The synapse, a minuscule gap between neurons, is where the magic of communication occurs. It’s the brain’s version of social media, a platform where neurons can ‘like,’ ‘share,’ and ‘comment’ on the signals they receive. This synaptic dialogue underpins every aspect of our being, from the mundane to the extraordinary.
The Chemical Messenger: Neurotransmitters
When an electrical impulse reaches a neuron’s axon terminal, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters, the brain’s chemical messengers. These molecules traverse the synaptic gap, carrying their message to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. This process can initiate or inhibit further electrical impulses, effectively deciding whether the message continues or ends.
The Role of Neurons and Synapses in Daily Life
The interaction between neurons and synapses is not just a matter of biological interest; it’s the foundation of our very experience. Whether you’re learning a new skill, enjoying your favorite song, or just deciding what to eat for lunch, neurons and synapses are hard at work. They’re the unsung heroes behind your ability to remember, feel, and interact with the world.
The Impact of Imbalance
Just as in any communication network, disruptions can have profound effects. An imbalance in neurotransmitter levels can lead to a range of psychological and neurological conditions, from depression and anxiety to Alzheimer’s disease. Understanding how synapses work not only fascinates us but also opens the door to groundbreaking treatments and therapies.
Preserving Our Neural Network
Maintaining the health of our neural communication systems is crucial. Lifestyle choices such as nutrition, exercise, stress management, and mental stimulation all play vital roles in keeping our neurons and synapses functioning optimally. In the digital era, where information overload is a constant, finding balance is key to preserving our mental health and cognitive abilities.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Neuroscience
As we delve deeper into the mysteries of the brain, the study of neurons and synapses stands on the cusp of new discoveries. With advancements in technology and research, we’re beginning to unlock the potential for healing and enhancing the human mind in ways previously imagined only in science fiction.
In this journey through the microscopic world of neurons and synapses, we’ve seen how these fundamental components shape our reality. The future of neuroscience promises not just a deeper understanding of ourselves but also the potential to improve the quality of life in unprecedented ways. As we stand at the intersection of biology and technology, one thing is clear: the exploration of the brain’s inner workings will continue to fascinate and inspire generations to come.